We provide diagnostic services of varying complexity at the LOR clinic by using modern examination methods and the latest generation equipment, thus ensuring accurate diagnosis, effective treatment and a careful approach to the health of each patient.
The examinations are performed by high-level specialists, paying special attention to the accuracy of the examination and the analysis of the obtained results.


If you have additional questions, please call +371 25 727 676 or write to us by e-mail: info@lorklinika.lv
The otolaryngologist (ear, throat and nose doctor) diagnoses and treats diseases of the nose, throat, nasopharynx and ears during the consultation, as well as prescribes additional examinations if required. For instance, the specialists of LOR clinic may prescribe the following examinations for patients with acute, chronic or recurrent ear, nose and throat diseases:

Dizziness is the feeling that the whole world revolves around you. It is usually accompanied by feeling unwell in the form of vomiting, nausea, imbalance and coordination disorders. Dizziness is the second most common patient complaint apart from headache. In most cases, a thorough collection of medical history and medical examination will help to specify the exact diagnosis and subsequent successful treatment. Most of these situations have a positive outcome. If dizziness is very severe, accompanied by loss of consciousness, difficulty swallowing and speaking, you should go to the hospital immediately.
However, most commonly, in about 70% of cases, the dizziness is caused by pathology of the inner ear. The other 30% may be related to neurological disorders, cardiovascular problems and other diseases.
In most cases, the first choice would be a visit to an otoneurologist, which, in a way, would serve as a guide for the resolution of your problems. An otoneurologist consults and treats patients in the events of dizziness. During the consultation, special tests and examinations are used by the doctor to differentiate the type of dizziness - vestibular (feeling that everything is turning around) or non-vestibular (feeling of imbalance). At the same time, the anatomical structure that causes the disorder - the cause of condition, is determined, because the treatment and outcome depend on it. It should be remembered that dizziness is one of the most non-homogeneous symptoms that requires careful investigation.

Both language and communication skills play a very important role in the life of a human. We use language to communicate with others, to express our emotions, to say that we love someone, and to solve problems. If the development of language is delayed, seek professional help. The first consultation with a speech therapist or an audio speech therapist lasts for about 45 minutes. During the consultation, history data are collected, tests of language comprehension, expressive vocabulary, sound pronunciation, phonetics (sound perception, word extraction, etc.) are performed.
At the same time, the research of speech motor skills is performed, the language system of the child (ability to form sentences grammatically correctly) is evaluated, as well as reading and writing skills are assessed. Based on the results of the examination, a conclusion is made and an agreement with parents on further cooperation is developed. During the examination, the audio speech therapist will assess:

In most cases, the assistance of a speech therapist or audio speech therapist is required if the following is observed:
Sessions of a speech therapist or an audio speech therapist are held once per week. Duration of each session: about 30-40 minutes, depending on the age of the child and their ability to concentrate. The presence of parents at the sessions is desirable in order to successfully consolidate the acquired skills at home.
The main directions of the audio speech therapist are as follows:
It is most often heard that an audio speech therapist helps children to “learn to speak correctly”, but these specialists also work with adults. There are several reasons why a person may have a speech disorder. Sometimes they appear as early as childhood, but at other times they occur after illness or an injury. In the event of voice disorders, the cause thereof will be important. The audio speech therapist only starts voice therapy pursuant to the recommendation of a physician. Depending on the cause, the therapy can be educational (on voice hygiene), voice restraining regimen, breathing exercises, exercises aimed at strengthening the neck and laryngeal muscles, voice exercises and vocal exercises.
A person with a language disorder may have difficulty speaking, understanding speech, reading or writing. There are several methods that you can use to improve your language. An appropriate method will be chosen depending on the purpose of treatment. Sessions of a speech therapist or audio speech therapist will be individual, however, the participation of family members is recommended to enable the use of what they have learnt in daily activities at home.
We all sometimes have difficulty swallowing, for instance, it takes extra effort to swallow a tough piece of meat. It is not infrequent to have a drink enter the airways and cause a person to choke and cough. People with swallowing disorders experience such situations frequently.
A paediatrician is a children’s doctor, who specialises in the diagnostics, treatment and prevention of children’s diseases. A paediatrician takes care of the healthy growth and development of children from birth to 18 years of age. At the same time, advice is provided on health prevention, vaccination, nutrition, exercise, cold exposure training, strengthening of immunity and other issues related to the health of children. If required, an additional investigation is prescribed. In the event of acute or chronic diseases, the paediatrician will provide prompt and comprehensive examination and therapy.
When visiting a paediatrician, all medical reports and conclusions related to the specific disease received at other medical institutions, as well as the immunisation passport and the results of the performed tests must be taken with you. This enables your doctor to receive the maximum amount of information, which facilitates the examination and diagnosing process of a child and helps to select the most appropriate therapy. Furthermore, this information saves time and resources, since some tests may have already been performed and may not need to be repeated. Parents are advised to timely prepare questions at home so that they do not forget something very important during the visit.
During the conversation with parents, the paediatrician examines the child and evaluates the results of the test and examination reports provided. At the same time, the doctor assesses the conformity of the weight and height of the child with their age. The doctor evaluates the complaints and specifies problems. If necessary, the paediatrician prescribes additional examinations, sends the child to consult with other specialists and makes arrangements for the next visit.
After the birth of a baby, the paediatrician will take professional, inclusive and individual care of the baby, providing advice on the development, feeding, care and disease prevention of the child.

Patients often complain of balance disorders or vertigo. Dizziness is a disturbing, unpleasant symptom that reduces your ability to work. This is a health problem that needs to be addressed. In most cases, a thorough history of the patient, a consultation of an otoneurologist and the performance of examinations helps to determine the exact diagnosis and successful subsequent therapy. In about 70% of all cases, vertigo is caused by pathology of the inner ear. The other 30% may be related to neurological disorders, cardiovascular problems and other diseases.
Patients often complain of balance disorders or vertigo. Dizziness is a disturbing, unpleasant symptom that reduces your ability to work. This is a health problem that needs to be addressed. In most cases, a thorough history of the patient, a consultation of an otoneurologist and the performance of examinations helps to determine the exact diagnosis and successful subsequent therapy. In about 70% of all cases, vertigo is caused by pathology of the inner ear. The other 30% may be related to neurological disorders, cardiovascular problems and other diseases.
The head impulse test is the only test that evaluates the vestibular-ocular reflex. This test helps to identify the cause of vertigo easily, quickly and non-invasively, and to start treatment. In addition to the head impulse test, audiometry and tympanometry may also be used.
The advantage of the head impulse test method is the accuracy of the diagnosis, which allows one to determine whether the problem of the patient is neurological or related to diseases of the inner ear. The examination is harmless and does not cause discomfort.
An allergologist will identify the causes of the allergy, as well as help with long-term difficulty breathing through the nose or rhinitis, redness of the eyes, conjunctivitis, skin rash that may be accompanied by itching, chronic indigestion, or long-term cough and shortness of breath. If necessary, a spirometry or skin allergy test can also be performed. The services are offered to children, as well as adults.

Allergen-specific immunotherapy is the only method of treatment that affects the causes of allergy. Long-term effects manifest after the completion of the therapy course.
Regardless of the type of immunotherapy, it relieves allergy symptoms within the first six months after the commencement of therapy. Initially, the medicinal product is prescribed, followed by a gradual increase of the dose. Then, administration of the medicine is continued at a constant maintenance dose. It is very important to follow the instructions of your physician precisely, when opting for immunotherapy. The average duration of therapy will be 3-5 years. When used properly, the effect of allergen-specific immunotherapy is retained after the medicinal product is discontinued - the symptoms decrease or even disappear. Efficacy, according to various medical literature sources, amounts to 70-85%, and that is a lot.
The main advantage of allergen-specific immunotherapy over anti-allergy drugs is that even during the first year of treatment, the manifestations of allergy and the need to use anti-allergy drugs - local glucocorticoids, antihistamines, etc., is reduced. Allergy medications quickly and successfully eliminate allergy symptoms, but if they are not used, the symptoms reappear. Meanwhile, allergen-specific immunotherapy is the only method of treatment that affects the causes of your allergy. Immunotherapy also prevents other allergies or allergic rhinitis from developing into bronchial asthma.
The objective of therapy is to reduce personal sensitivity to an allergen by gradually altering the immune response of the body and ensuring resistance to the allergen. The body is gradually accustomed to the allergen that it does not tolerate. For instance, if the allergy is caused by a dust mite or pollen, then the patient, in the long run, receives the medicinal product that gradually accustoms the body to these allergens. The same is true if you are allergic to bee or wasp stings, animal dander, mould, etc. To achieve this objective, patients should carefully follow the instructions of their doctor during immunotherapy.
During the consultation, the hearing acoustician will evaluate the results of the hearing test, as well as the individual daily requirements of the patient, and find the most suitable technical solution to reduce hearing loss.
At the same time, hearing aids will be adapted to the level of hearing and explanations regarding the capabilities and functions thereof will be provided. If required, individual earplugs will be made to ensure the comprehensive use of hearing aids. The duration of the first consultation is approximately 1 hour.

During the consultation, the hearing acoustician will insert a hearing aid into your ear. It will be adjusted to the degree of your hearing impairment and a volume setting that is acceptable to you will be selected. Furthermore, you will receive detailed explanations on how to use the hearing aid: how to put it in your ear, and how to control the volume. The specialist will also tell you how to care for your hearing aid, how to replace the batteries, as well as how to clean it and dry it. Finally, a specialist will explain to you how the hearing aid responds to different situations. Then you will be able to go home with your new hearing aid.
In the first few days, you will need to get used to your new hearing aid. At first, use it for a few hours a day in a familiar environment. Some things will seem unusual. The best way to test your new hearing aid is to talk to people or watch TV. You will find your own voice unusual or too loud because you were used to speaking loud in order to hear yourself. Try to speak a little quieter. Write down your sensations - this will help your doctor adjust the hearing aid to the appropriate volume level.
Repeated hearing acoustics consultation, or adjustment of hearing aids, is usually prescribed two weeks after the first consultation to improve comfort and the speech perception of the patient. Based on patient feedback, the specialist will perform additional adjustment of the hearing aids, as well as the necessary actions to ensure the comprehensive use of technical aids. A hearing acoustician will answer all your questions and provide the advice you need. To improve your comfort and speech perception, your hearing aid will be adjusted during the consultation.

Accurate, instrumental hearing sharpness test performed with an electro-acoustic device - audiometer.
Audiometry examinations are required to:Tone audiometry tests both air conduction and bone conduction. What does it mean? Air conduction is tested by using special headphones, with sound reaching the inner ear through the outer ear canal and the middle ear cavity. Bone conduction is tested by means of a special speaker, which is placed directly behind the ear, on the mastoid process. In this way, a sound signal is played on the bone and measurements are made to determine how the auditory nerve works in the event of bone conduction.
With the resulting air conduction curve, we can determine if there is a sulphur plug in the outer ear that has clogged the duct; furthermore, an immobile eardrum can affect the conduction of sound to the internal structures of the brain and there can also be many other air conduction diseases. It is important for us to check bone conductivity to determine the quality of the auditory nerve, furthermore, this measurement shows age-related hearing loss, otosclerosis and other diseases.
Tone audiometry test method requires the test subject to be able to concentrate and engage as much as possible to get results, so this measurement is recommended in children starting from 4 to 5 years of age, provided that the child has age-appropriate intelligence and communication skills.
Free field audiometry is suitable for children under 4 years of age. If free field audiometry is used to determine the threshold of hearing for both ears, then Tone audiometry shall be used to determine the threshold of hearing for each ear separately, because hearing rarely deteriorates equally and simultaneously in both ears. There are situations, where a person hears well with one ear, while the hearing with the other ear is worse, and then the results of Tone audiometry are very important.
As a result of tone audiometry, you obtain an audiogram (graphic image) with air and bone conduction curves for each ear separately. This information is later used by an ENT specialist or a hearing acoustician.
Headphones are placed on the ears, through which sound signals are given. When the patient hears an audible signal, he/she presses the button, confirming that he/she has heard the given sound. The volume and pitch are being changed. The result of the hearing test is a graph (audiogram) showing the nature and degree of hearing impairment. Based on the results of the examinations, the doctor diagnoses various degrees of hearing impairment. The procedure is comfortable and painless.
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure as a result of which palatine tonsils - two oval-shaped formations of lymphoid tissue in the back of the throat - each on its own side, are removed.
In the past, tonsillectomy was a more common procedure to treat inflammation and infections of palatine tonsils. Today, tonsillectomy is performed to treat obstructive sleep apnoea and chronic inflammation of palatine tonsils that does not respond to conservative treatment.
Why is this being performed?- Recurrent, chronic or severe tonsillitis (angina)
Due to enlarged palatine tonsils (sleep apnoea)
In the event of peritonsillar abscess – a condition where pus accumulates behind the tonsil tissue due to inflammation, and neither drainage nor antibiotic therapy are effective.
- Reaction to anaesthesia. Medications that are administered to the patient to enable them to sleep can cause temporary side effects - headache, nausea, vomiting. More serious side effects after the administration of anaesthetic medication are rare.
- Pain and swelling in the area of the tongue and throat - may cause difficulty breathing. The most pronounced pain and swelling occurs on day 2 to 3 after surgery. It is recommended to use plenty of fluids, preferably water (2-3 l per day).
- Circulation during surgery and the post-surgical period. Bleeding is much easier to stop during surgery. In the postsurgical period, bleeding is usually observed on day seven and day fourteen, which is associated with the formation of scabs. The regimen prescribed by your doctor must be strictly observed.
- The risk of postsurgical infection is very low, pale yellow plaques in the throat are a sign of a normal healing process and antibacterial therapy is required in very rare cases after surgery.
How do you prepare for the surgery?
- Ask relatives, if anyone has had an allergic reaction during general anaesthesia, or if the patient or someone in the family has had blood clotting problems. Find out if anyone in the family has allergic reactions to medications, as well as whether they themselves (parents) know about possible allergic reactions.
- When arriving for the operation, it is necessary to take the following test results with you:
Complete blood count, blood coagulation profile (APTT, prothrombin, INR), blood chemistry (ASAT, ALAT. Urea, creatinine, glucose, protein, electrolytes), electrocardiogram with a description (adults), pulmonary X-Ray (with description, valid for 1 year).
- To reduce the risk of bleeding, the administration of blood thinners (aspirin, orfarin, etc.) should be discontinued two weeks before the planned operation. For women - the surgery should not be performed during menstruation, especially during the first three days.
- You must come to the operation on an empty stomach. It is forbidden to eat or drink on the day of the operation!
- Adults need to arrange transportation home, because the patient must not drive after the operation, and there must be someone to accompany the patient at home.
- A 10-14 day home regimen should be considered. Restricted physical activity and diet, which will be described in detail by the operating physician. Children usually have a less complicated postsurgical period, especially in the event of a tonsillotomy (partial removal of the tonsils) compared to a tonsillectomy (complete removal of the tonsils).
- It usually lasts up to one hour, but this can vary due to the development of scar tissue, bleeding and other factors.
- the operation is conducted under general anaesthesia, so the patient does not feel any pain during it.
- To ensure access to the palatine tonsils, a special mouth extender is inserted, which helps to open the mouth and then fixed in position. Then an incision in the tonsillar bed is made and the tonsil is peeled from the tonsillar niches with the tonsillar capsule. Usually, only a part of the palatine tonsil is removed in children (if there are complaints of snoring, sleep apnoea, clinically enlarged size of tonsils). Electrocoagulation is used to stop the bleeding, and if required, palate beds are sewn together. The control of the operation site is performed and the operation is completed.
- Postsurgical pain is inevitable, usually in the area of the palatine tonsils; the pain often radiates to the ears, jaw and neck.
- The set of measures that should be followed to reduce pain and speed up recovery is as follows:
- Bleeding - admixture of fresh blood in saliva, spitting of blood clots is an indication to seek emergency medical attention.
- Increased body temperature and fever - contact your attending physician or general practitioner to prescribe the therapy you need.
- Difficult breathing - snoring or 'snivelling' is normal in the first week after surgery, but if you or your child has difficulty breathing, you need urgent medical attention.
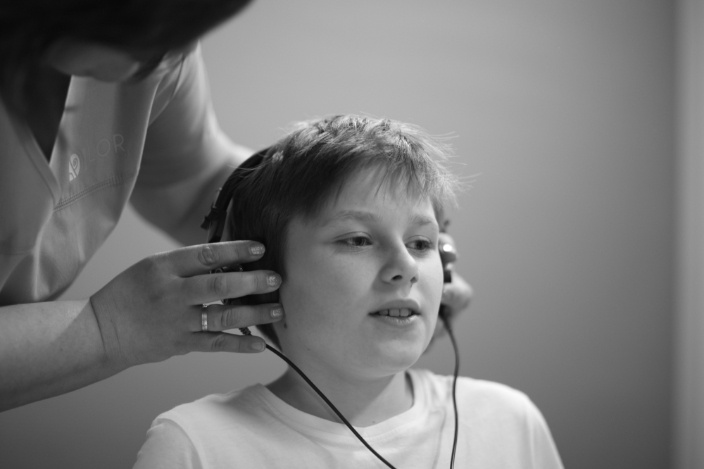

Free field audiometry is a screening method that enables accurate and early detection of hearing deterioration in both children and adults. Free field audiometry, unlike other types of audiometry, determines the total hearing threshold in both ears simultaneously. What does it mean? During this measurement, a person listens to sound signals of different frequencies and volumes with both ears simultaneously. As a result, we obtain an audiogram, which shows the volume and frequency at which a person hears best, and what the frequencies are, where hearing is impaired. It is important to understand why a person does not hear speech, because each sound has its own volume (in dB) and frequency (in Hz). For example, high frequency sounds - S, F, K, T are within the frequency range of 2000 to 8000 Hz, while sounds - Z, M, D, B, etc. are within the frequency range of 250 to 1000 Hz. The fundamental sound frequencies or frequencies at which a person hears best are 250, 500 and 1000 Hz. High-frequency sounds are affected more often, therefore, a person ceases to perceive speech.
An adult understands speech with a slight hearing loss better than a child, because the adult already has well developed speech, as well as the ability to “lip read” is more pronounced in adults in the event of hearing loss. The development of a child's speech takes place in a certain order, and if the child's hearing decreases, the development is impaired, so it is important to detect hearing impairments promptly.
Free field audiometry is performed for both children and adults with or without hearing aids/cochlear implants. For a person with hearing aids/cochlear implants, the performance of free field audiometry is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the hearing aid.
Free field audiometry is performed by using an audiometer that reproduces sounds of different heights and volumes with the help of loudspeakers. The task of the patient is to concentrate and respond to a barely audible sound. The examination is performed in a specially designed audiometry office, which is insulated with special soundproof material. A remote control is given to the patient. As soon as a person hears a barely audible sound, their task is to press the button.
The purpose of free field audiometry is to promptly detect hearing loss in order to apply an appropriate technical hearing aid. At very high hearing losses (that is losses above 100 dB reduction), the technical aids would involve hearing implants. At lower hearing losses (up to 100 dB reduction), they would be hearing aids. An audiogram is required by a hearing acoustician and an ENT specialist to determine hearing loss or to adjust hearing aids individually for a child or an adult.

Quick hearing test by using a tuning fork (usually 256 Hz or 512 Hz). The Rinne and Weber tests are used most commonly. The Weber test is a screening test of hearing. It can be used to identify unilateral conduction-type hearing loss, i.e. (middle ear hearing loss) and unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, i.e. (inner ear hearing loss).
The test is performed by placing a tuning fork in the centre of the patient's forehead on the hairline or at the base of the nose. The patient is then asked whether the sound is louder in one of the ears, or if he/she hears it on the midline.
Meanwhile, the Rinne test, on the other hand, is used to examine the difference between air sound conduction and bone conduction. The tuning fork is placed on the mastoid process and the bone conduction is checked, but the fork is placed next to the ear to determine air conduction. The patient identifies which stimulation method produces a louder sound. If the patient has hearing loss, the sound perception is better on the mastoid process. If the patient notes a difference between the ears, moving on to the Weber test is necessary to identify sensorineural hearing loss. These methods are absolutely painless, as well as easy and quick to perform.
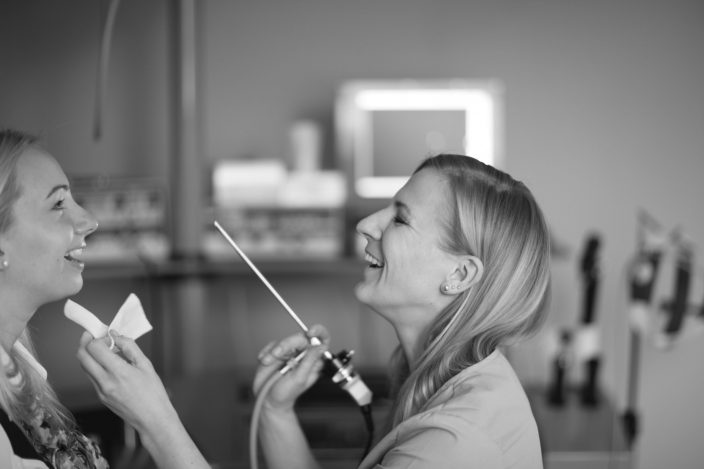
Diagnostic method used to examine the middle ear. This method determines the pressure in the tympanic cavity, the eardrums and the mobility of the auditory ossicles. Tympanometry helps to diagnose various diseases in cases where nothing is detected with the use of classical ENT instruments. Examples include otitis media, otosclerosis, fluid and adhesions in the tympanic cavity.

A video device for the evaluation of nasal mucosa, anatomical structures, evaluation of the natural openings of sinuses, as well as diagnosis of nasopharyngeal pathologies. A 2 mm flexible nasopharyngeal endoscope, as well as 2 mm all-angle rigid endoscopes are used at LOR clinic. The method is performed under local anaesthesia.

Nasal irrigation is an additional therapeutic method for the therapy of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses. Nasal irrigation, i.e. - the extraction of mucus and pus by using a vacuum pump, which reduces inflammation. Patients acknowledge that immediate respiratory relief is experienced. The procedure is not painful, but causes slight discomfort.
For the sake of clarity, it must be added that nasal irrigation is not associated with the need to perform a puncture. It is the rinsing of nasal and nasopharyngeal discharge with saline solution or, if necessary, with medicinal products. In most cases, this procedure provides good results and allows for effective recovery without the use of antibiotics. However, only a physician during the examination can tell whether the patient needs it or not, since there will be no result.
Vacuum irrigation is most commonly used for children. Medications are administered through one nostril, and secretions accumulated in the paranasal sinuses are expelled through the other with the help of a vacuum. Vacuum rinsing should normally be repeated at least four to five times.

Removing/rinsing of the plugs does not hurt, unless you have already tried to clean the ear by hand with cotton swabs, and injured the ear canals. Sulphur plugs are rinsed by means of warm water jet pressure. Nowadays, sulphur plugs are rinsed by means of a special rinsing device or a hook for the removal of foreign bodies.
Please be reminded that the release of sulphur is the protective reaction of the body against dust, foreign bodies, as well as microbes and fungal infections that can get into the ears. The release of sulphur by every person differs, just like the sweat glands of each person function differently - some of us perspire a lot, others almost not at all. If an increased amount of sulphur production is observed in a child, it is nothing bad, it is just a normal physiological reaction of the body.

Tympanic membrane massage is performed with a special device designed for the physiotherapy of secretory inflammations of the middle ear. Pressure and vibration is used to mobilise tympanic membranes, which promotes the removal of fluid from the tympanic cavity. At the same time, pain, tinnitus are reduced, as well as hearing perception is stimulated. The procedure lasts for 5-15 minutes.

If a child or adult bleeds only once, there is no reason to worry about their health. However, if it starts to recur regularly and there are other health problems, for instance, a lot of haematomas or wounds in the event of bruises, or scratches bleed for a long time, it is imperative to see a doctor and to determine the cause of bleeding.
Method to stop bleeding that is based on the effect of electricity (cauterisation or burning of blood vessels). It can be used under both local and general anaesthesia. It is most commonly used to stop nosebleeds.
To stop the bleeding in a home setting, the head should be tilted forwards instead of backwards. Both nostrils should be compressed close with your fingers and held for 7-10 minutes. This is the normal blood clotting time. At the same time, something cold can be placed on the root of the nose (place between the eyes) or in the nape area. To stop nosebleeds, do not put cotton swabs in your nose, as changing them every minute will not allow a blood clot to form in the injured area of the blood vessel to keep the wound closed.

Have you ever had a situation, where there are several people around who are talking, and one of them asks you for something, but you cannot understand what they are saying? Or have you noticed that your child is unable to learn while sitting with the TV on or that his/her school performance is deteriorating? This phenomenon can be explained by various theories, but one of the most popular is Central auditory processing disorder. These are disorders that manifest themselves in situations where, against a background noise, a person is unable to focus on the work to be done or listen to what the desired person is saying. Diagnosis of these disorders is complicated, but not impossible.
To identify central auditory processing disorder, the evaluation of complex sound hearing threshold, namely speech perception, is required. Therefore, instead of playing tones, language signals, such as syllables, words, numbers, or sentences, are played back during language audiometry.
When performing language audiometry, speech signals are played in both or one ear. A masking noise is played at the same time. This noise is called white noise, which is set at a certain volume and frequency to assess a person's ability to distinguish speech in that noise. Dichotic tests, which involve the simultaneous reproduction of different signals in both ears, are very important. What does it mean? The word “two” is pronounced in one ear and “ten” is simultaneously sounded in the other ear. It is the task of the customer to name these two numbers, which is not that simple.
Language audiometry is used not only to evaluate hearing impairment, but also the effectiveness of hearing aids and cochlear implants. Thus, the hearing aid user is able to understand whether the hearing aid can help them to hear speech not only in a quiet, but also a noisy environment, such as a conference, cafe, etc. However, the clinical significance of speech audiometry lies in the identification of central auditory processing disorder.
It is important to diagnose these disorders in order to be able to adapt to the environment afterwards, especially for children both at home and at school. If a person has a central auditory processing disorder diagnosis, one solution is an assistive device, namely an FM device, which is especially helpful for students in hearing what the teacher is saying better, since it reduces ambient noise. This device also helps people with hearing aids to better perceive what is said by other people, irrespective of the environment.
Language audiometry test takes 30-60 minutes. The results of language audiometry are explained to the patient and further therapy solutions are suggested. This is a unique opportunity, because, finally, a test in Latvian is available in Latvia, which provides a lot of information to help people with central auditory processing disorder.

Adenoidectomy or surgery of the nasopharyngeal tonsil
All children are born with nasopharyngeal tonsils, which do not affect the normal function of nasal breathing, and, at the age of five to six, they begins to gradually regress in their development. Meanwhile, at the age of puberty, atrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsils begins, as a result of which, they completely disappear by the age of twenty. If a child under the age of five to six often suffers from upper respiratory tract infections, the nasopharyngeal tonsils increase in volume, making it difficult to breathe through the nose; in this case, it is called an adenoid. Adenoids indirectly affect other organs and organ systems, for instance, the openings in the hearing canal, causing the child to have hearing loss.
Enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil is a relatively common phenomenon in childhood. Usually, the situation begins to improve as the child reaches adolescence, however, in some cases the problem persists into adulthood.
Problems breathing through the nose and other problems in children with adenoids
Diagnosis of adenoids is based on:
complaints of difficult breathing through the nose, snoring at night or during sleep, sleeping with open mouth, frequent or persistent runny nose, recurrent ear pain or hearing loss, deterioration of hearing, tiredness and poor learning, speech disorders and nocturnal enuresis.
An absolute indication for adenoidectomy is an enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil with subsequent obstructive sleep apnoea(snoring of a child resulting in intermittent sleep apnoea). Other indications for adenoidectomy is a secretory inflammation of the middle ear (accumulation of liquid in the middle ear – impaired hearing), frequent inflammations of the middle ear, as well as enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil and chronic inflammations of the paranasal sinuses.
If necessary, adenoidectomy is performed in conjunction with tonsillotomy (reduction of the tonsils of the palate) and tympanostomy (insertion of ventilation tubes into the tympanic membranes).
If a child often suffers from inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, then adenoidectomy may be one of the possible treatment options to reduce the incidence of the disease.
Adenoidectomy is performed in cases of chronic otitis media.
How to prepare for the surgery:
- Blood tests should be performed before the operation - complete blood count, blood coagulation profile.
- Before the operation, tell the physician everything about the medical history of the child (medications the child is taking, chronic illnesses, allergic reactions, if any, family illness history, i.e. congenital illnesses, etc.).
How to help your child prepare:
- Try to explain why it is necessary - tell them that after the procedure it will be possible to breathe better through the nose, that they will be sick less frequently, and that they will hear better.
- Explain that special medications will help them sleep without feeling pain.
- Allow your child to take their favourite item or blanket with them; anything that makes them feel comfortable.
Procedure of the operation:
Adenoidectomy is a short surgical operation in terms of time and is usually performed at a day-care hospital.
- It is performed under general anaesthesia, so your child will not feel any pain during the operation.
- To access the nasopharyngeal tonsil, the surgeon will insert a special mouthpiece that will keep the child's mouth open during sleep, then evacuate the nasopharyngeal tonsil; electrocoagulation can be used to prevent nasopharyngeal bleeding.
- After the procedure, the child shall be observed until they wake up. If there are no complications, the child is taken to their parents and is allowed to go home in a few hours. After the procedure, the child is highly likely to be drowsy, possibly, having nausea caused by anaesthetic medication.
The postsurgical period is usually well tolerated by children. The child needs a gentle home regimen - hot food and drinks should be avoided, soft, blended food should be eaten for ~ 2 weeks, the child has to avoid hot showers, baths or saunas. The patient needs to drink plenty of fluids per day (~ 2-3 l); the more fluid your child consumes, the easier and faster the recovery process will be. There may be an unpleasant odour from the mouth after surgery; this is due to healing.
What are the cases, where a specialist must be consulted as an emergency procedure?
- Fresh blood through the nose or mouth.
- The child does not eat or drink, has a reduced amount of urine, cries without tears.
- Persistent pain, hearing or balance disorders.

Deguna starpsienas operācija (septoplastika) ir ķirurģiska manipulācija, kuras laikā tiek iztaisnotas deguna kaula un deguna starpsienas skrimšļainās daļas. Ja starpsiena, kas atdala abas nāsis, ir izliekta, to dēvē par deviētu deguna starpsienu. Šā iemesla dēļ var būt apgrūtināta elpošana caur degunu, paaugstināts deguna blakusdobumu iekaisumu risks, kā arī augstāks hroniska vidusauss iekaisuma risks.
Veicot deguna starpsienas operāciju, tiek izgrieztas un iztaisnotas deviētās daļas. Pēc deguna starpsienas operācijas pacients labāk elpo caur degunu.
Deviēta deguna starpsiena ir bieži sastopama. Ļoti izteikti deviēta deguna starpsiena var apgrūtināt elpošanu caur vienu vai pat abām nāsīm, kas ietekmē dzīves kvalitāti. Bieži deguna starpsienas deviācija ir saistīta ar deguna gliemežnīcu palielināšanos (hipertrofiju) šādos gadījumos nereti pacients kļūst atkarīgs no deguna pilieniem, kuri samazina tūsku.
Lai precīzi noteiktu operācijas apjomu, pirms operācijas būtu ieteicams veikt datortomogrāfiju, lai izvērtētu deguna starpsienas, deguna gliemežnīcu un deguna blakusdobumu stāvokli.
Operācijas riski
Tāpat kā jebkurai citai operācijai, arī deguna starpsienas operācijai ir savi riski, neskaitot asiņošanu, infekciju un reakciju uz anestēzijas medikamentiem. Iespējamās deguna starpsienas operācijas komplikācijas:
- saglabājas deguna aizlikums;
- pastiprināta asiņošana no deguna;
- deguna formas pārmaiņas;
- deguna starpsienas perforācija (caurums deguna starpsienā pēc operācijas, kas saistīts ar dzīšanas procesu un neizbēgamu asinsvadu traumatizāciju operācijas laikā);
- ožas pārmaiņas (parasti pārejošas);
- receklis deguna ejās, kuru nepieciešams evakuēt;
- pārejošs cieto aukslēju un augšējo zobu nejutīgums vai sāpes.
Pirms tiek plānota operācija, ar ķirurgu tiek izrunāti operācijas ieguvumi un iespējamās komplikācijas.
- Ierodoties uz operāciju, līdzi jāņem analīžu un citu izmeklējumu rezultāti:
pilna asinsaina, asins koagulogramma (APTL, protrombīns, INR), asins bioķīmija (ASAT, ALAT, urea, kreatinīns, glikoze, olbaltumvielas, elektrolīti), elektrokardiogramma ar aprakstu (pieaugušajiem), plaušu rentgenogramma (ar aprakstu, derīga 1 gadu).
- Lai samazinātu asiņošanas risku, divas nedēļas pirms plānotās operācijas ir jāpārtrauc lietot asinis šķidrinoši medikamenti (aspirīns, orfarīns u.c.). Sievietēm jāņem vērā, ka operāciju nedrīkst veikt menstruāciju laikā, īpaši pirmo trīs dienu laikā.
- Uz operāciju jāierodas tukšā dūšā. Operācijas dienā ir aizliegts ēst un dzert!
- Pieaugušajiem nepieciešams organizēt transportu mājup, jo pacients pats pēc operācijas nedrīkst sēsties pie stūres, kā arī obligāti jābūt kādam, kurš pacientu pavada mājās.
Operācija parasti tiek veikta vispārējā anestēzijā. Operācijas laikā veic griezienu vienā no nāsīm deguna iekšpusē. Tiek evakuētas izlocītās skrimšļainās un kaulainās daļās. Ja nepieciešams, veic arī deguna gliemežnīcu operāciju, lai samazinātu to izmērus. Pēc deguna starpsienas iztaisnošanas deguna ejās ievieto silikona plāksnītes vai hemostatiskos sūklīšus, lai samazinātu asiņošanas risku, kā arī lai operācijas efekts būtu labāks. Šos materiālus ķirurgs evakuēs nākamajā nozīmētajā vizītē.
Pēc operācijas:Lai samazinātu pēcoperācijas asiņošanas un tūskas risku, jūsu ārsts var lūgt ievērot noteiktu režīmu pāris nedēļu pēc operācijas:
- pacelt galvgali gulēšanas laikā;
- stipri nešņaukt degunu;
- ievērot miera režīmu. Ierobežotas fiziskās aktivitātes;
- nelidot ar lidmašīnu 14 dienas pēc operācijas;
- nepieciešamības gadījumā lietot pretsāpju medikamentus;
- izvairīties no karstiem ēdieniem un dzērieniem;
- neiet karstā vannā, dušā;
- ārsta noteiktu laika periodu neapmeklēt pirti, saunu;
- veikt deguna eju kopšanu (pēc ārsta rekomendācijām).
- Pēc operācijas ir iespējama asiņošana no deguna, mājas apstākļos var palīdzēt aukstuma kompreses uz pieres vai uz spranda. Ja asiņošanu neizdodas apturēt, jāmeklē medicīniskā palīdzība. Ne vienmēr rezultāts parādās uzreiz, tas ir atkarīgs no katra individuāli. Parasti 3–6 mēnešu laikā viss nostājas “vecajā” vietā, un, ja tas rada sūdzības, var apsvērt atkārtotu deguna starpsienas operāciju. Lielākā daļa pacientu, kam tiek veikta deguna starpsienas operācija, atzīmē, ka elpošana caur degunu ir uzlabojusies, kā arī samazinājies deguna blakusdobumu iekaisumu skaits.

Ventilation tubes or tympanostomy cannulas are small plastic or metal tubes that are inserted into the eardrums. These tubes provide ventilation to the middle ear, thus preventing fluid from accumulating behind the tympanic membrane. Tube insertion is recommended for patients (usually children) with fluid in the middle ear (secretory otitis), especially in cases where the child has impaired hearing and delayed development of speech; furthermore, tube insertion is recommended if the patient has frequent and/or chronic otitis media. Often the tubes fall out after 6-9 months themselves, or they are removed after 1-1.5 years.
Under normal conditions, ventilation in the middle ear occurs through the auditory canal (Eustachian tube), which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx. This channel regulates air pressure, refreshes air and drains secretions from the middle ear.
The development of inflammation and formation of mucus in the auditory canal as a result of inflammation or allergic reactions can lead to the closure of the auditory canal and the build-up of fluid in the middle ear. Usually, it affects children because the auditory canal in children is more horizontal and narrower than in adults - these factors contribute to drainage problems and canal blockage.
Insertion of ventilation tubes is an alternative way of providing air access to the middle ear, as well as reducing the pressure in it. Tubes are inserted in the cases
Risks:Insertion of a ventilation tube is a relatively safe procedure with a low risk of serious complications. Potential complications:
- Bleeding and infection
- Constant drainage of fluid from the ear
- Failure of the function of the ventilation tube due to blood clot, mucus or other secretions
- Self-evacuation of the tube occurs too early
- After the tube drops out or is removed, a hole remains in the eardrum which fails heal itself
In children, this operation is usually performed under general mask anaesthesia, during which the child does not feel any pain. In adults, this operation can also be performed under local anaesthesia with infiltration anaesthesia in the mastoid region, in a way that is similar to anaesthesia used by a dentist.
Potential complications of anaesthesia are very rare and include allergic reactions, difficult breathing, heart function disorders, nausea and vomiting after surgery.
How to prepare for the surgery:- Blood tests should be performed before the operation - complete blood count, blood coagulation profile.
- Before the operation, tell the physician everything about the medical history of the child (medications the child is taking, chronic illnesses, allergic reactions (if any), family disease history – potential congenital diseases).
- Try to explain why it is necessary - tell them that after the procedure the ears will feel better, or that they will be able to hear much better.
- Explain that special medications will help them sleep without feeling pain during the insertion of the tubes.
- Allow your child to take their favourite item or blanket with them; anything that makes them feel comfortable.
- Anaesthesia - the operation is performed under general anaesthesia, thus, the child will not feel pain. Several monitors are installed on the child to monitor and, if required, to regulate the heart rate, blood pressure, and the amount of oxygen in the blood of the child.
- The procedure lasts for 10-15 minutes. A small incision is made in the eardrum, the exsufflation of fluid from the middle ear is performed and the ventilation tube is inserted through the incision site.
After the procedure, the child shall be observed until they wake up. If there are no complications, the child is taken to their parents and is allowed to go home in a few hours. After the procedure, the child is highly likely to be drowsy, possibly, having nausea caused by anaesthetic medication. After ~ 24 h a child returns to their usual daily routine. Usually after the procedure, the child or the parents immediately notice an improvement in hearing. There is a possibility of pain after the insertion of the tubes, any analgesic medicine for the paediatric population is suitable for the prevention thereof.
Observation:- In the standard case, your doctor is likely to make an appointment with an ENT specialist within 2-4 weeks after the insertion of the tubes. The next appointment is scheduled in 4-6 months.
- After the procedure, a hearing test may be prescribed, if you have had a history of hearing loss.
- The requirement to protect the ears of the child from water is unlikely, unless instructed otherwise by their attending physician.
- Yellow, brown or bloody discharge from the ear for more than 1 week after tube insertion.
- Persistent pain, hearing or balance disorders.
- The risk of otitis media is reduced (It should be noted that the insertion of ventilation tubes does not protect against all middle ear inflammations).
-Hearing is restored or improved.
- The child's speech improves.

Loss of voice should not last for more than two weeks. In addition to seasonal viruses, hoarseness or loss of voice can be caused by other diseases, for instance, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, when the oesophagus does not close, meaning that the patient develops a reflux of stomach acid or enzymes that reaches the vocal cords, causing irritation and voice hoarseness.
At the same time, phonation is adversely affected by smoking. With regular smoking, mucus begins to form more intensively, which settles on the vocal cords; the mucus becomes thicker, therefore the timbre of the voice changes, and it becomes harsher.
Voice hoarseness often occurs in people who overload their vocal cords on a daily basis, for instance, teachers, while in singers, especially those who have failed to master proper singing techniques, the development of knots on the vocal cords can be the cause of a dull voice. This can be caused by a variety of laryngeal injuries, such as thyroid surgery, which damages a nerve that allows the larynx and ligaments to move.
In the event of acute and chronic inflammation of the vocal cords, various combinations of oils and medications are applied to the vocal cords under visual control. Special laryngeal syringes are used during the procedure.

The otolaryngologist (ear, throat and nose doctor) diagnoses and treats diseases of the nose, throat, nasopharynx and ears during the consultation, as well as prescribes additional examinations if required. For instance, the specialists of LOR clinic may prescribe the following examinations for patients with acute, chronic or recurrent ear, nose and throat diseases:

Dizziness is the feeling that the whole world revolves around you. It is usually accompanied by feeling unwell in the form of vomiting, nausea, imbalance and coordination disorders. Dizziness is the second most common patient complaint apart from headache. In most cases, a thorough collection of medical history and medical examination will help to specify the exact diagnosis and subsequent successful treatment. Most of these situations have a positive outcome. If dizziness is very severe, accompanied by loss of consciousness, difficulty swallowing and speaking, you should go to the hospital immediately.
However, most commonly, in about 70% of cases, the dizziness is caused by pathology of the inner ear. The other 30% may be related to neurological disorders, cardiovascular problems and other diseases.
In most cases, the first choice would be a visit to an otoneurologist, which, in a way, would serve as a guide for the resolution of your problems. An otoneurologist consults and treats patients in the events of dizziness. During the consultation, special tests and examinations are used by the doctor to differentiate the type of dizziness – vestibular (feeling that everything is turning around) or non-vestibular (feeling of imbalance). At the same time, the anatomical structure that causes the disorder – the cause of condition, is determined, because the treatment and outcome depend on it. It should be remembered that dizziness is one of the most non-homogeneous symptoms that requires careful investigation.

Both language and communication skills play a very important role in the life of a human. We use language to communicate with others, to express our emotions, to say that we love someone, and to solve problems. If the development of language is delayed, seek professional help. The first consultation with a speech therapist or an audio speech therapist lasts for about 45 minutes. During the consultation, history data are collected, tests of language comprehension, expressive vocabulary, sound pronunciation, phonetics (sound perception, word extraction, etc.) are performed.
At the same time, the research of speech motor skills is performed, the language system of the child (ability to form sentences grammatically correctly) is evaluated, as well as reading and writing skills are assessed. Based on the results of the examination, a conclusion is made and an agreement with parents on further cooperation is developed. During the examination, the audio speech therapist will assess:

In most cases, the assistance of a speech therapist or audio speech therapist is required if the following is observed:
Sessions of a speech therapist or an audio speech therapist are held once per week. Duration of each session: about 30-40 minutes, depending on the age of the child and their ability to concentrate. The presence of parents at the sessions is desirable in order to successfully consolidate the acquired skills at home.
The main directions of the audio speech therapist are as follows:
Speech disorders
It is most often heard that an audio speech therapist helps children to “learn to speak correctly”, but these specialists also work with adults. There are several reasons why a person may have a speech disorder. Sometimes they appear as early as childhood, but at other times they occur after illness or an injury. In the event of voice disorders, the cause thereof will be important. The audio speech therapist only starts voice therapy pursuant to the recommendation of a physician. Depending on the cause, the therapy can be educational (on voice hygiene), voice restraining regimen, breathing exercises, exercises aimed at strengthening the neck and laryngeal muscles, voice exercises and vocal exercises.
Language disorders
A person with a language disorder may have difficulty speaking, understanding speech, reading or writing. There are several methods that you can use to improve your language. An appropriate method will be chosen depending on the purpose of treatment. Sessions of a speech therapist or audio speech therapist will be individual, however, the participation of family members is recommended to enable the use of what they have learnt in daily activities at home.
Swallowing disorders
We all sometimes have difficulty swallowing, for instance, it takes extra effort to swallow a tough piece of meat. It is not infrequent to have a drink enter the airways and cause a person to choke and cough. People with swallowing disorders experience such situations frequently.

A paediatrician is a children’s doctor, who specialises in the diagnostics, treatment and prevention of children’s diseases. A paediatrician takes care of the healthy growth and development of children from birth to 18 years of age. At the same time, advice is provided on health prevention, vaccination, nutrition, exercise, cold exposure training, strengthening of immunity and other issues related to the health of children. If required, an additional investigation is prescribed. In the event of acute or chronic diseases, the paediatrician will provide prompt and comprehensive examination and therapy.
How do you prepare for the visit?
When visiting a paediatrician, all medical reports and conclusions related to the specific disease received at other medical institutions, as well as the immunisation passport and the results of the performed tests must be taken with you. This enables your doctor to receive the maximum amount of information, which facilitates the examination and diagnosing process of a child and helps to select the most appropriate therapy. Furthermore, this information saves time and resources, since some tests may have already been performed and may not need to be repeated. Parents are advised to timely prepare questions at home so that they do not forget something very important during the visit.
What is the procedure of a visit like?
During the conversation with parents, the paediatrician examines the child and evaluates the results of the test and examination reports provided. At the same time, the doctor assesses the conformity of the weight and height of the child with their age. The doctor evaluates the complaints and specifies problems. If necessary, the paediatrician prescribes additional examinations, sends the child to consult with other specialists and makes arrangements for the next visit.
After the birth of a baby, the paediatrician will take professional, inclusive and individual care of the baby, providing advice on the development, feeding, care and disease prevention of the child.

Patients often complain of balance disorders or vertigo. Dizziness is a disturbing, unpleasant symptom that reduces your ability to work. This is a health problem that needs to be addressed. In most cases, a thorough history of the patient, a consultation of an otoneurologist and the performance of examinations helps to determine the exact diagnosis and successful subsequent therapy. In about 70% of all cases, vertigo is caused by pathology of the inner ear. The other 30% may be related to neurological disorders, cardiovascular problems and other diseases.
Patients often complain of balance disorders or vertigo. Dizziness is a disturbing, unpleasant symptom that reduces your ability to work. This is a health problem that needs to be addressed. In most cases, a thorough history of the patient, a consultation of an otoneurologist and the performance of examinations helps to determine the exact diagnosis and successful subsequent therapy. In about 70% of all cases, vertigo is caused by pathology of the inner ear. The other 30% may be related to neurological disorders, cardiovascular problems and other diseases.
The head impulse test is the only test that evaluates the vestibular-ocular reflex. This test helps to identify the cause of vertigo easily, quickly and non-invasively, and to start treatment. In addition to the head impulse test, audiometry and tympanometry may also be used.
The advantage of the head impulse test method is the accuracy of the diagnosis, which allows one to determine whether the problem of the patient is neurological or related to diseases of the inner ear. The examination is harmless and does not cause discomfort.

An allergologist will identify the causes of the allergy, as well as help with long-term difficulty breathing through the nose or rhinitis, redness of the eyes, conjunctivitis, skin rash that may be accompanied by itching, chronic indigestion, or long-term cough and shortness of breath. If necessary, a spirometry or skin allergy test can also be performed. The services are offered to children, as well as adults.

Allergen-specific immunotherapy is the only method of treatment that affects the causes of allergy. Long-term effects manifest after the completion of the therapy course.
Regardless of the type of immunotherapy, it relieves allergy symptoms within the first six months after the commencement of therapy. Initially, the medicinal product is prescribed, followed by a gradual increase of the dose. Then, administration of the medicine is continued at a constant maintenance dose. It is very important to follow the instructions of your physician precisely, when opting for immunotherapy. The average duration of therapy will be 3-5 years. When used properly, the effect of allergen-specific immunotherapy is retained after the medicinal product is discontinued – the symptoms decrease or even disappear. Efficacy, according to various medical literature sources, amounts to 70-85%, and that is a lot.
The main advantage of allergen-specific immunotherapy over anti-allergy drugs is that even during the first year of treatment, the manifestations of allergy and the need to use anti-allergy drugs – local glucocorticoids, antihistamines, etc., is reduced. Allergy medications quickly and successfully eliminate allergy symptoms, but if they are not used, the symptoms reappear. Meanwhile, allergen-specific immunotherapy is the only method of treatment that affects the causes of your allergy. Immunotherapy also prevents other allergies or allergic rhinitis from developing into bronchial asthma.
The objective of therapy is to reduce personal sensitivity to an allergen by gradually altering the immune response of the body and ensuring resistance to the allergen. The body is gradually accustomed to the allergen that it does not tolerate. For instance, if the allergy is caused by a dust mite or pollen, then the patient, in the long run, receives the medicinal product that gradually accustoms the body to these allergens. The same is true if you are allergic to bee or wasp stings, animal dander, mould, etc. To achieve this objective, patients should carefully follow the instructions of their doctor during immunotherapy.

During the consultation, the hearing acoustician will evaluate the results of the hearing test, as well as the individual daily requirements of the patient, and find the most suitable technical solution to reduce hearing loss.
At the same time, hearing aids will be adapted to the level of hearing and explanations regarding the capabilities and functions thereof will be provided. If required, individual earplugs will be made to ensure the comprehensive use of hearing aids. The duration of the first consultation is approximately 1 hour.

During the consultation, the hearing acoustician will insert a hearing aid into your ear. It will be adjusted to the degree of your hearing impairment and a volume setting that is acceptable to you will be selected. Furthermore, you will receive detailed explanations on how to use the hearing aid: how to put it in your ear, and how to control the volume. The specialist will also tell you how to care for your hearing aid, how to replace the batteries, as well as how to clean it and dry it. Finally, a specialist will explain to you how the hearing aid responds to different situations. Then you will be able to go home with your new hearing aid.
The first steps in using a hearing aid
In the first few days, you will need to get used to your new hearing aid. At first, use it for a few hours a day in a familiar environment. Some things will seem unusual. The best way to test your new hearing aid is to talk to people or watch TV. You will find your own voice unusual or too loud because you were used to speaking loud in order to hear yourself. Try to speak a little quieter. Write down your sensations – this will help your doctor adjust the hearing aid to the appropriate volume level.
Repeated hearing acoustics consultation, or adjustment of hearing aids, is usually prescribed two weeks after the first consultation to improve comfort and the speech perception of the patient. Based on patient feedback, the specialist will perform additional adjustment of the hearing aids, as well as the necessary actions to ensure the comprehensive use of technical aids. A hearing acoustician will answer all your questions and provide the advice you need. To improve your comfort and speech perception, your hearing aid will be adjusted during the consultation.

Accurate, instrumental hearing sharpness test performed with an electro-acoustic device – audiometer.
Audiometry examinations are required to:
Tone audiometry tests both air conduction and bone conduction. What does it mean? Air conduction is tested by using special headphones, with sound reaching the inner ear through the outer ear canal and the middle ear cavity. Bone conduction is tested by means of a special speaker, which is placed directly behind the ear, on the mastoid process. In this way, a sound signal is played on the bone and measurements are made to determine how the auditory nerve works in the event of bone conduction.
With the resulting air conduction curve, we can determine if there is a sulphur plug in the outer ear that has clogged the duct; furthermore, an immobile eardrum can affect the conduction of sound to the internal structures of the brain and there can also be many other air conduction diseases. It is important for us to check bone conductivity to determine the quality of the auditory nerve, furthermore, this measurement shows age-related hearing loss, otosclerosis and other diseases.
Tone audiometry test method requires the test subject to be able to concentrate and engage as much as possible to get results, so this measurement is recommended in children starting from 4 to 5 years of age, provided that the child has age-appropriate intelligence and communication skills.
Free field audiometry is suitable for children under 4 years of age. If free field audiometry is used to determine the threshold of hearing for both ears, then Tone audiometry shall be used to determine the threshold of hearing for each ear separately, because hearing rarely deteriorates equally and simultaneously in both ears. There are situations, where a person hears well with one ear, while the hearing with the other ear is worse, and then the results of Tone audiometry are very important.
As a result of tone audiometry, you obtain an audiogram (graphic image) with air and bone conduction curves for each ear separately. This information is later used by an ENT specialist or a hearing acoustician.
Examination procedure:
Headphones are placed on the ears, through which sound signals are given. When the patient hears an audible signal, he/she presses the button, confirming that he/she has heard the given sound. The volume and pitch are being changed. The result of the hearing test is a graph (audiogram) showing the nature and degree of hearing impairment. Based on the results of the examinations, the doctor diagnoses various degrees of hearing impairment. The procedure is comfortable and painless.

Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure as a result of which palatine tonsils – two oval-shaped formations of lymphoid tissue in the back of the throat – each on its own side, are removed.
In the past, tonsillectomy was a more common procedure to treat inflammation and infections of palatine tonsils. Today, tonsillectomy is performed to treat obstructive sleep apnoea and chronic inflammation of palatine tonsils that does not respond to conservative treatment.
Why is this being performed?
– Recurrent, chronic or severe tonsillitis (angina)
Due to enlarged palatine tonsils (sleep apnoea)
In the event of peritonsillar abscess – a condition where pus accumulates behind the tonsil tissue due to inflammation, and neither drainage nor antibiotic therapy are effective.
– Reaction to anaesthesia. Medications that are administered to the patient to enable them to sleep can cause temporary side effects – headache, nausea, vomiting. More serious side effects after the administration of anaesthetic medication are rare.
– Pain and swelling in the area of the tongue and throat – may cause difficulty breathing. The most pronounced pain and swelling occurs on day 2 to 3 after surgery. It is recommended to use plenty of fluids, preferably water (2-3 l per day).
– Circulation during surgery and the post-surgical period. Bleeding is much easier to stop during surgery. In the postsurgical period, bleeding is usually observed on day seven and day fourteen, which is associated with the formation of scabs. The regimen prescribed by your doctor must be strictly observed.
– The risk of postsurgical infection is very low, pale yellow plaques in the throat are a sign of a normal healing process and antibacterial therapy is required in very rare cases after surgery.
How do you prepare for the surgery?
– Ask relatives, if anyone has had an allergic reaction during general anaesthesia, or if the patient or someone in the family has had blood clotting problems. Find out if anyone in the family has allergic reactions to medications, as well as whether they themselves (parents) know about possible allergic reactions.
– When arriving for the operation, it is necessary to take the following test results with you:
Complete blood count, blood coagulation profile (APTT, prothrombin, INR), blood chemistry (ASAT, ALAT. Urea, creatinine, glucose, protein, electrolytes), electrocardiogram with a description (adults), pulmonary X-Ray (with description, valid for 1 year).
– To reduce the risk of bleeding, the administration of blood thinners (aspirin, orfarin, etc.) should be discontinued two weeks before the planned operation. For women – the surgery should not be performed during menstruation, especially during the first three days.
– You must come to the operation on an empty stomach. It is forbidden to eat or drink on the day of the operation!
– Adults need to arrange transportation home, because the patient must not drive after the operation, and there must be someone to accompany the patient at home.
– A 10-14 day home regimen should be considered. Restricted physical activity and diet, which will be described in detail by the operating physician. Children usually have a less complicated postsurgical period, especially in the event of a tonsillotomy (partial removal of the tonsils) compared to a tonsillectomy (complete removal of the tonsils).
Procedure of the operation:
– It usually lasts up to one hour, but this can vary due to the development of scar tissue, bleeding and other factors.
– the operation is conducted under general anaesthesia, so the patient does not feel any pain during it.
– To ensure access to the palatine tonsils, a special mouth extender is inserted, which helps to open the mouth and then fixed in position. Then an incision in the tonsillar bed is made and the tonsil is peeled from the tonsillar niches with the tonsillar capsule. Usually, only a part of the palatine tonsil is removed in children (if there are complaints of snoring, sleep apnoea, clinically enlarged size of tonsils). Electrocoagulation is used to stop the bleeding, and if required, palate beds are sewn together. The control of the operation site is performed and the operation is completed.
Recovery period:
– Postsurgical pain is inevitable, usually in the area of the palatine tonsils; the pain often radiates to the ears, jaw and neck.
– The set of measures that should be followed to reduce pain and speed up recovery is as follows:
When should emergency medical attention be sought?
– Bleeding – admixture of fresh blood in saliva, spitting of blood clots is an indication to seek emergency medical attention.
– Increased body temperature and fever – contact your attending physician or general practitioner to prescribe the therapy you need.
– Difficult breathing – snoring or ‘snivelling’ is normal in the first week after surgery, but if you or your child has difficulty breathing, you need urgent medical attention.

Free field audiometry is a screening method that enables accurate and early detection of hearing deterioration in both children and adults. Free field audiometry, unlike other types of audiometry, determines the total hearing threshold in both ears simultaneously. What does it mean? During this measurement, a person listens to sound signals of different frequencies and volumes with both ears simultaneously. As a result, we obtain an audiogram, which shows the volume and frequency at which a person hears best, and what the frequencies are, where hearing is impaired. It is important to understand why a person does not hear speech, because each sound has its own volume (in dB) and frequency (in Hz). For example, high frequency sounds – S, F, K, T are within the frequency range of 2000 to 8000 Hz, while sounds – Z, M, D, B, etc. are within the frequency range of 250 to 1000 Hz. The fundamental sound frequencies or frequencies at which a person hears best are 250, 500 and 1000 Hz. High-frequency sounds are affected more often, therefore, a person ceases to perceive speech.
An adult understands speech with a slight hearing loss better than a child, because the adult already has well developed speech, as well as the ability to “lip read” is more pronounced in adults in the event of hearing loss. The development of a child’s speech takes place in a certain order, and if the child’s hearing decreases, the development is impaired, so it is important to detect hearing impairments promptly.
Free field audiometry is performed for both children and adults with or without hearing aids/cochlear implants. For a person with hearing aids/cochlear implants, the performance of free field audiometry is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the hearing aid.
Free field audiometry is performed by using an audiometer that reproduces sounds of different heights and volumes with the help of loudspeakers. The task of the patient is to concentrate and respond to a barely audible sound. The examination is performed in a specially designed audiometry office, which is insulated with special soundproof material. A remote control is given to the patient. As soon as a person hears a barely audible sound, their task is to press the button.
The purpose of free field audiometry is to promptly detect hearing loss in order to apply an appropriate technical hearing aid. At very high hearing losses (that is losses above 100 dB reduction), the technical aids would involve hearing implants. At lower hearing losses (up to 100 dB reduction), they would be hearing aids. An audiogram is required by a hearing acoustician and an ENT specialist to determine hearing loss or to adjust hearing aids individually for a child or an adult.

Quick hearing test by using a tuning fork (usually 256 Hz or 512 Hz). The Rinne and Weber tests are used most commonly. The Weber test is a screening test of hearing. It can be used to identify unilateral conduction-type hearing loss, i.e. (middle ear hearing loss) and unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, i.e. (inner ear hearing loss).
The test is performed by placing a tuning fork in the centre of the patient’s forehead on the hairline or at the base of the nose. The patient is then asked whether the sound is louder in one of the ears, or if he/she hears it on the midline.
Meanwhile, the Rinne test, on the other hand, is used to examine the difference between air sound conduction and bone conduction. The tuning fork is placed on the mastoid process and the bone conduction is checked, but the fork is placed next to the ear to determine air conduction. The patient identifies which stimulation method produces a louder sound. If the patient has hearing loss, the sound perception is better on the mastoid process. If the patient notes a difference between the ears, moving on to the Weber test is necessary to identify sensorineural hearing loss. These methods are absolutely painless, as well as easy and quick to perform.

Diagnostic method used to examine the middle ear. This method determines the pressure in the tympanic cavity, the eardrums and the mobility of the auditory ossicles. Tympanometry helps to diagnose various diseases in cases where nothing is detected with the use of classical ENT instruments. Examples include otitis media, otosclerosis, fluid and adhesions in the tympanic cavity.

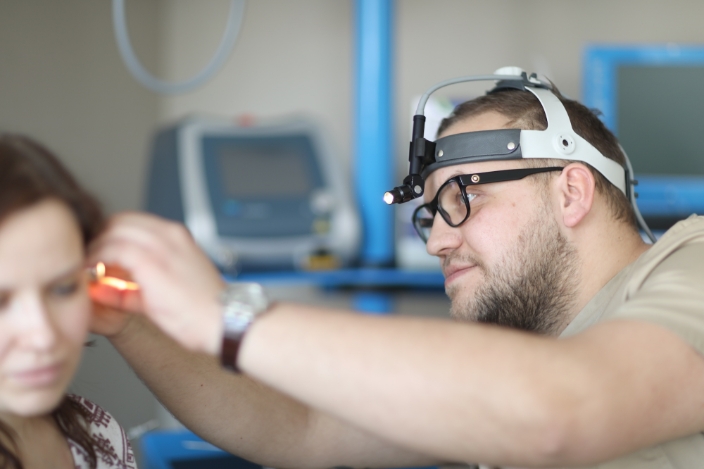
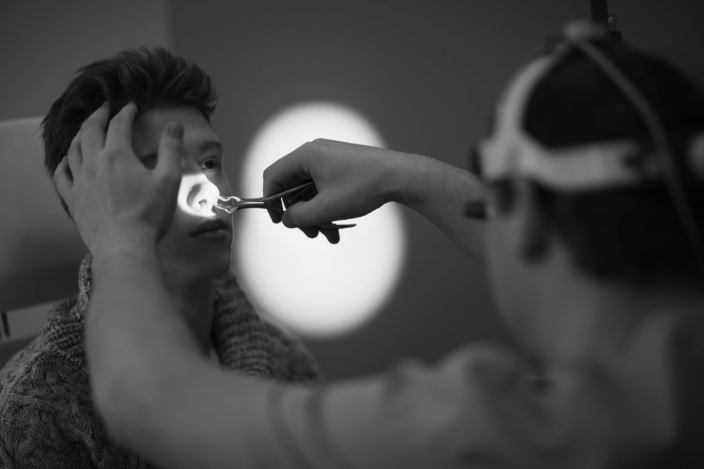
A video device for the evaluation of nasal mucosa, anatomical structures, evaluation of the natural openings of sinuses, as well as diagnosis of nasopharyngeal pathologies. A 2 mm flexible nasopharyngeal endoscope, as well as 2 mm all-angle rigid endoscopes are used at LOR clinic. The method is performed under local anaesthesia.

Nasal irrigation is an additional therapeutic method for the therapy of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses. Nasal irrigation, i.e. – the extraction of mucus and pus by using a vacuum pump, which reduces inflammation. Patients acknowledge that immediate respiratory relief is experienced. The procedure is not painful, but causes slight discomfort.
For the sake of clarity, it must be added that nasal irrigation is not associated with the need to perform a puncture. It is the rinsing of nasal and nasopharyngeal discharge with saline solution or, if necessary, with medicinal products. In most cases, this procedure provides good results and allows for effective recovery without the use of antibiotics. However, only a physician during the examination can tell whether the patient needs it or not, since there will be no result.
Vacuum irrigation is most commonly used for children. Medications are administered through one nostril, and secretions accumulated in the paranasal sinuses are expelled through the other with the help of a vacuum. Vacuum rinsing should normally be repeated at least four to five times.

Removing/rinsing of the plugs does not hurt, unless you have already tried to clean the ear by hand with cotton swabs, and injured the ear canals. Sulphur plugs are rinsed by means of warm water jet pressure. Nowadays, sulphur plugs are rinsed by means of a special rinsing device or a hook for the removal of foreign bodies.
Please be reminded that the release of sulphur is the protective reaction of the body against dust, foreign bodies, as well as microbes and fungal infections that can get into the ears. The release of sulphur by every person differs, just like the sweat glands of each person function differently – some of us perspire a lot, others almost not at all. If an increased amount of sulphur production is observed in a child, it is nothing bad, it is just a normal physiological reaction of the body.

Tympanic membrane massage is performed with a special device designed for the physiotherapy of secretory inflammations of the middle ear. Pressure and vibration is used to mobilise tympanic membranes, which promotes the removal of fluid from the tympanic cavity. At the same time, pain, tinnitus are reduced, as well as hearing perception is stimulated. The procedure lasts for 5-15 minutes.

If a child or adult bleeds only once, there is no reason to worry about their health. However, if it starts to recur regularly and there are other health problems, for instance, a lot of haematomas or wounds in the event of bruises, or scratches bleed for a long time, it is imperative to see a doctor and to determine the cause of bleeding.
Method to stop bleeding that is based on the effect of electricity (cauterisation or burning of blood vessels). It can be used under both local and general anaesthesia. It is most commonly used to stop nosebleeds.
To stop the bleeding in a home setting, the head should be tilted forwards instead of backwards. Both nostrils should be compressed close with your fingers and held for 7-10 minutes. This is the normal blood clotting time. At the same time, something cold can be placed on the root of the nose (place between the eyes) or in the nape area. To stop nosebleeds, do not put cotton swabs in your nose, as changing them every minute will not allow a blood clot to form in the injured area of the blood vessel to keep the wound closed.

Have you ever had a situation, where there are several people around who are talking, and one of them asks you for something, but you cannot understand what they are saying? Or have you noticed that your child is unable to learn while sitting with the TV on or that his/her school performance is deteriorating? This phenomenon can be explained by various theories, but one of the most popular is Central auditory processing disorder. These are disorders that manifest themselves in situations where, against a background noise, a person is unable to focus on the work to be done or listen to what the desired person is saying. Diagnosis of these disorders is complicated, but not impossible.
To identify central auditory processing disorder, the evaluation of complex sound hearing threshold, namely speech perception, is required. Therefore, instead of playing tones, language signals, such as syllables, words, numbers, or sentences, are played back during language audiometry.
When performing language audiometry, speech signals are played in both or one ear. A masking noise is played at the same time. This noise is called white noise, which is set at a certain volume and frequency to assess a person’s ability to distinguish speech in that noise. Dichotic tests, which involve the simultaneous reproduction of different signals in both ears, are very important. What does it mean? The word “two” is pronounced in one ear and “ten” is simultaneously sounded in the other ear. It is the task of the customer to name these two numbers, which is not that simple.
Language audiometry is used not only to evaluate hearing impairment, but also the effectiveness of hearing aids and cochlear implants. Thus, the hearing aid user is able to understand whether the hearing aid can help them to hear speech not only in a quiet, but also a noisy environment, such as a conference, cafe, etc. However, the clinical significance of speech audiometry lies in the identification of central auditory processing disorder.
It is important to diagnose these disorders in order to be able to adapt to the environment afterwards, especially for children both at home and at school. If a person has a central auditory processing disorder diagnosis, one solution is an assistive device, namely an FM device, which is especially helpful for students in hearing what the teacher is saying better, since it reduces ambient noise. This device also helps people with hearing aids to better perceive what is said by other people, irrespective of the environment.
Language audiometry test takes 30-60 minutes. The results of language audiometry are explained to the patient and further therapy solutions are suggested. This is a unique opportunity, because, finally, a test in Latvian is available in Latvia, which provides a lot of information to help people with central auditory processing disorder.

Adenoidectomy or surgery of the nasopharyngeal tonsil
All children are born with nasopharyngeal tonsils, which do not affect the normal function of nasal breathing, and, at the age of five to six, they begins to gradually regress in their development. Meanwhile, at the age of puberty, atrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsils begins, as a result of which, they completely disappear by the age of twenty. If a child under the age of five to six often suffers from upper respiratory tract infections, the nasopharyngeal tonsils increase in volume, making it difficult to breathe through the nose; in this case, it is called an adenoid. Adenoids indirectly affect other organs and organ systems, for instance, the openings in the hearing canal, causing the child to have hearing loss.
Enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil is a relatively common phenomenon in childhood. Usually, the situation begins to improve as the child reaches adolescence, however, in some cases the problem persists into adulthood.
Problems breathing through the nose and other problems in children with adenoids
Diagnostics of adenoids
Diagnosis of adenoids is based on:
complaints of difficult breathing through the nose, snoring at night or during sleep, sleeping with open mouth, frequent or persistent runny nose, recurrent ear pain or hearing loss, deterioration of hearing, tiredness and poor learning, speech disorders and nocturnal enuresis.
An absolute indication for adenoidectomy is an enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil with subsequent obstructive sleep apnoea(snoring of a child resulting in intermittent sleep apnoea). Other indications for adenoidectomy is a secretory inflammation of the middle ear (accumulation of liquid in the middle ear – impaired hearing), frequent inflammations of the middle ear, as well as enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil and chronic inflammations of the paranasal sinuses.
If necessary, adenoidectomy is performed in conjunction with tonsillotomy (reduction of the tonsils of the palate) and tympanostomy (insertion of ventilation tubes into the tympanic membranes).
If a child often suffers from inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, then adenoidectomy may be one of the possible treatment options to reduce the incidence of the disease.
Adenoidectomy is performed in cases of chronic otitis media.
How to prepare for the surgery:
– Blood tests should be performed before the operation – complete blood count, blood coagulation profile.
– Before the operation, tell the physician everything about the medical history of the child (medications the child is taking, chronic illnesses, allergic reactions, if any, family illness history, i.e. congenital illnesses, etc.).
How to help your child prepare:
– Try to explain why it is necessary – tell them that after the procedure it will be possible to breathe better through the nose, that they will be sick less frequently, and that they will hear better.
– Explain that special medications will help them sleep without feeling pain.
– Allow your child to take their favourite item or blanket with them; anything that makes them feel comfortable.
Procedure of the operation:
Adenoidectomy is a short surgical operation in terms of time and is usually performed at a day-care hospital.
– It is performed under general anaesthesia, so your child will not feel any pain during the operation.
– To access the nasopharyngeal tonsil, the surgeon will insert a special mouthpiece that will keep the child’s mouth open during sleep, then evacuate the nasopharyngeal tonsil; electrocoagulation can be used to prevent nasopharyngeal bleeding.
– After the procedure, the child shall be observed until they wake up. If there are no complications, the child is taken to their parents and is allowed to go home in a few hours. After the procedure, the child is highly likely to be drowsy, possibly, having nausea caused by anaesthetic medication.
The postsurgical period is usually well tolerated by children. The child needs a gentle home regimen – hot food and drinks should be avoided, soft, blended food should be eaten for ~ 2 weeks, the child has to avoid hot showers, baths or saunas. The patient needs to drink plenty of fluids per day (~ 2-3 l); the more fluid your child consumes, the easier and faster the recovery process will be. There may be an unpleasant odour from the mouth after surgery; this is due to healing.
What are the cases, where a specialist must be consulted as an emergency procedure?
– Fresh blood through the nose or mouth.
– The child does not eat or drink, has a reduced amount of urine, cries without tears.
– Persistent pain, hearing or balance disorders.

Deguna starpsienas operācija (septoplastika) ir ķirurģiska manipulācija, kuras laikā tiek iztaisnotas deguna kaula un deguna starpsienas skrimšļainās daļas. Ja starpsiena, kas atdala abas nāsis, ir izliekta, to dēvē par deviētu deguna starpsienu. Šā iemesla dēļ var būt apgrūtināta elpošana caur degunu, paaugstināts deguna blakusdobumu iekaisumu risks, kā arī augstāks hroniska vidusauss iekaisuma risks.
Veicot deguna starpsienas operāciju, tiek izgrieztas un iztaisnotas deviētās daļas. Pēc deguna starpsienas operācijas pacients labāk elpo caur degunu.
Deviēta deguna starpsiena ir bieži sastopama. Ļoti izteikti deviēta deguna starpsiena var apgrūtināt elpošanu caur vienu vai pat abām nāsīm, kas ietekmē dzīves kvalitāti. Bieži deguna starpsienas deviācija ir saistīta ar deguna gliemežnīcu palielināšanos (hipertrofiju) šādos gadījumos nereti pacients kļūst atkarīgs no deguna pilieniem, kuri samazina tūsku.
Lai precīzi noteiktu operācijas apjomu, pirms operācijas būtu ieteicams veikt datortomogrāfiju, lai izvērtētu deguna starpsienas, deguna gliemežnīcu un deguna blakusdobumu stāvokli.
Operācijas riski
Tāpat kā jebkurai citai operācijai, arī deguna starpsienas operācijai ir savi riski, neskaitot asiņošanu, infekciju un reakciju uz anestēzijas medikamentiem. Iespējamās deguna starpsienas operācijas komplikācijas:
– saglabājas deguna aizlikums;
– pastiprināta asiņošana no deguna;
– deguna formas pārmaiņas;
– deguna starpsienas perforācija (caurums deguna starpsienā pēc operācijas, kas saistīts ar dzīšanas procesu un neizbēgamu asinsvadu traumatizāciju operācijas laikā);
– ožas pārmaiņas (parasti pārejošas);
– receklis deguna ejās, kuru nepieciešams evakuēt;
– pārejošs cieto aukslēju un augšējo zobu nejutīgums vai sāpes.
Kā sagatavoties:
Pirms tiek plānota operācija, ar ķirurgu tiek izrunāti operācijas ieguvumi un iespējamās komplikācijas.
– Ierodoties uz operāciju, līdzi jāņem analīžu un citu izmeklējumu rezultāti:
pilna asinsaina, asins koagulogramma (APTL, protrombīns, INR), asins bioķīmija (ASAT, ALAT, urea, kreatinīns, glikoze, olbaltumvielas, elektrolīti), elektrokardiogramma ar aprakstu (pieaugušajiem), plaušu rentgenogramma (ar aprakstu, derīga 1 gadu).
– Lai samazinātu asiņošanas risku, divas nedēļas pirms plānotās operācijas ir jāpārtrauc lietot asinis šķidrinoši medikamenti (aspirīns, orfarīns u.c.). Sievietēm jāņem vērā, ka operāciju nedrīkst veikt menstruāciju laikā, īpaši pirmo trīs dienu laikā.
– Uz operāciju jāierodas tukšā dūšā. Operācijas dienā ir aizliegts ēst un dzert!
– Pieaugušajiem nepieciešams organizēt transportu mājup, jo pacients pats pēc operācijas nedrīkst sēsties pie stūres, kā arī obligāti jābūt kādam, kurš pacientu pavada mājās.
Operācijas norise:
Operācija parasti tiek veikta vispārējā anestēzijā. Operācijas laikā veic griezienu vienā no nāsīm deguna iekšpusē. Tiek evakuētas izlocītās skrimšļainās un kaulainās daļās. Ja nepieciešams, veic arī deguna gliemežnīcu operāciju, lai samazinātu to izmērus. Pēc deguna starpsienas iztaisnošanas deguna ejās ievieto silikona plāksnītes vai hemostatiskos sūklīšus, lai samazinātu asiņošanas risku, kā arī lai operācijas efekts būtu labāks. Šos materiālus ķirurgs evakuēs nākamajā nozīmētajā vizītē.
Pēc operācijas:
Lai samazinātu pēcoperācijas asiņošanas un tūskas risku, jūsu ārsts var lūgt ievērot noteiktu režīmu pāris nedēļu pēc operācijas:
– pacelt galvgali gulēšanas laikā;
– stipri nešņaukt degunu;
– ievērot miera režīmu. Ierobežotas fiziskās aktivitātes;
– nelidot ar lidmašīnu 14 dienas pēc operācijas;
– nepieciešamības gadījumā lietot pretsāpju medikamentus;
– izvairīties no karstiem ēdieniem un dzērieniem;
– neiet karstā vannā, dušā;
– ārsta noteiktu laika periodu neapmeklēt pirti, saunu;
– veikt deguna eju kopšanu (pēc ārsta rekomendācijām).
Kad nepieciešams apmeklēt ārstu ārpus kārtas?
– Pēc operācijas ir iespējama asiņošana no deguna, mājas apstākļos var palīdzēt aukstuma kompreses uz pieres vai uz spranda. Ja asiņošanu neizdodas apturēt, jāmeklē medicīniskā palīdzība.
Ne vienmēr rezultāts parādās uzreiz, tas ir atkarīgs no katra individuāli. Parasti 3–6 mēnešu laikā viss nostājas “vecajā” vietā, un, ja tas rada sūdzības, var apsvērt atkārtotu deguna starpsienas operāciju.
Lielākā daļa pacientu, kam tiek veikta deguna starpsienas operācija, atzīmē, ka elpošana caur degunu ir uzlabojusies, kā arī samazinājies deguna blakusdobumu iekaisumu skaits.

Ventilation tubes or tympanostomy cannulas are small plastic or metal tubes that are inserted into the eardrums. These tubes provide ventilation to the middle ear, thus preventing fluid from accumulating behind the tympanic membrane. Tube insertion is recommended for patients (usually children) with fluid in the middle ear (secretory otitis), especially in cases where the child has impaired hearing and delayed development of speech; furthermore, tube insertion is recommended if the patient has frequent and/or chronic otitis media. Often the tubes fall out after 6-9 months themselves, or they are removed after 1-1.5 years.
Under normal conditions, ventilation in the middle ear occurs through the auditory canal (Eustachian tube), which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx. This channel regulates air pressure, refreshes air and drains secretions from the middle ear.
The development of inflammation and formation of mucus in the auditory canal as a result of inflammation or allergic reactions can lead to the closure of the auditory canal and the build-up of fluid in the middle ear. Usually, it affects children because the auditory canal in children is more horizontal and narrower than in adults – these factors contribute to drainage problems and canal blockage.
Insertion of ventilation tubes is an alternative way of providing air access to the middle ear, as well as reducing the pressure in it. Tubes are inserted in the cases
Risks:
Insertion of a ventilation tube is a relatively safe procedure with a low risk of serious complications. Potential complications:
– Bleeding and infection
– Constant drainage of fluid from the ear
– Failure of the function of the ventilation tube due to blood clot, mucus or other secretions
– Self-evacuation of the tube occurs too early
– After the tube drops out or is removed, a hole remains in the eardrum which fails heal itself
Procedure of the operation:
In children, this operation is usually performed under general mask anaesthesia, during which the child does not feel any pain. In adults, this operation can also be performed under local anaesthesia with infiltration anaesthesia in the mastoid region, in a way that is similar to anaesthesia used by a dentist.
Potential complications of anaesthesia are very rare and include allergic reactions, difficult breathing, heart function disorders, nausea and vomiting after surgery.
How to prepare for the surgery:
– Blood tests should be performed before the operation – complete blood count, blood coagulation profile.
– Before the operation, tell the physician everything about the medical history of the child (medications the child is taking, chronic illnesses, allergic reactions (if any), family disease history – potential congenital diseases).
How to help your child prepare:
– Try to explain why it is necessary – tell them that after the procedure the ears will feel better, or that they will be able to hear much better.
– Explain that special medications will help them sleep without feeling pain during the insertion of the tubes.
– Allow your child to take their favourite item or blanket with them; anything that makes them feel comfortable.
Procedure of the operation:
– Anaesthesia – the operation is performed under general anaesthesia, thus, the child will not feel pain. Several monitors are installed on the child to monitor and, if required, to regulate the heart rate, blood pressure, and the amount of oxygen in the blood of the child.
– The procedure lasts for 10-15 minutes. A small incision is made in the eardrum, the exsufflation of fluid from the middle ear is performed and the ventilation tube is inserted through the incision site.
After the procedure, the child shall be observed until they wake up. If there are no complications, the child is taken to their parents and is allowed to go home in a few hours. After the procedure, the child is highly likely to be drowsy, possibly, having nausea caused by anaesthetic medication. After ~ 24 h a child returns to their usual daily routine. Usually after the procedure, the child or the parents immediately notice an improvement in hearing. There is a possibility of pain after the insertion of the tubes, any analgesic medicine for the paediatric population is suitable for the prevention thereof.
Observation:
– In the standard case, your doctor is likely to make an appointment with an ENT specialist within 2-4 weeks after the insertion of the tubes. The next appointment is scheduled in 4-6 months.
– After the procedure, a hearing test may be prescribed, if you have had a history of hearing loss.
– The requirement to protect the ears of the child from water is unlikely, unless instructed otherwise by their attending physician.
What are the cases, where a specialist must be consulted as an emergency procedure?
– Yellow, brown or bloody discharge from the ear for more than 1 week after tube insertion.
– Persistent pain, hearing or balance disorders.
As a result – ventilation tubes provide ventilation and drainage in the middle ear:
– The risk of otitis media is reduced (It should be noted that the insertion of ventilation tubes does not protect against all middle ear inflammations).
-Hearing is restored or improved.
– The child’s speech improves.

Loss of voice should not last for more than two weeks. In addition to seasonal viruses, hoarseness or loss of voice can be caused by other diseases, for instance, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, when the oesophagus does not close, meaning that the patient develops a reflux of stomach acid or enzymes that reaches the vocal cords, causing irritation and voice hoarseness.
At the same time, phonation is adversely affected by smoking. With regular smoking, mucus begins to form more intensively, which settles on the vocal cords; the mucus becomes thicker, therefore the timbre of the voice changes, and it becomes harsher.
Voice hoarseness often occurs in people who overload their vocal cords on a daily basis, for instance, teachers, while in singers, especially those who have failed to master proper singing techniques, the development of knots on the vocal cords can be the cause of a dull voice. This can be caused by a variety of laryngeal injuries, such as thyroid surgery, which damages a nerve that allows the larynx and ligaments to move.
In the event of acute and chronic inflammation of the vocal cords, various combinations of oils and medications are applied to the vocal cords under visual control. Special laryngeal syringes are used during the procedure.